About
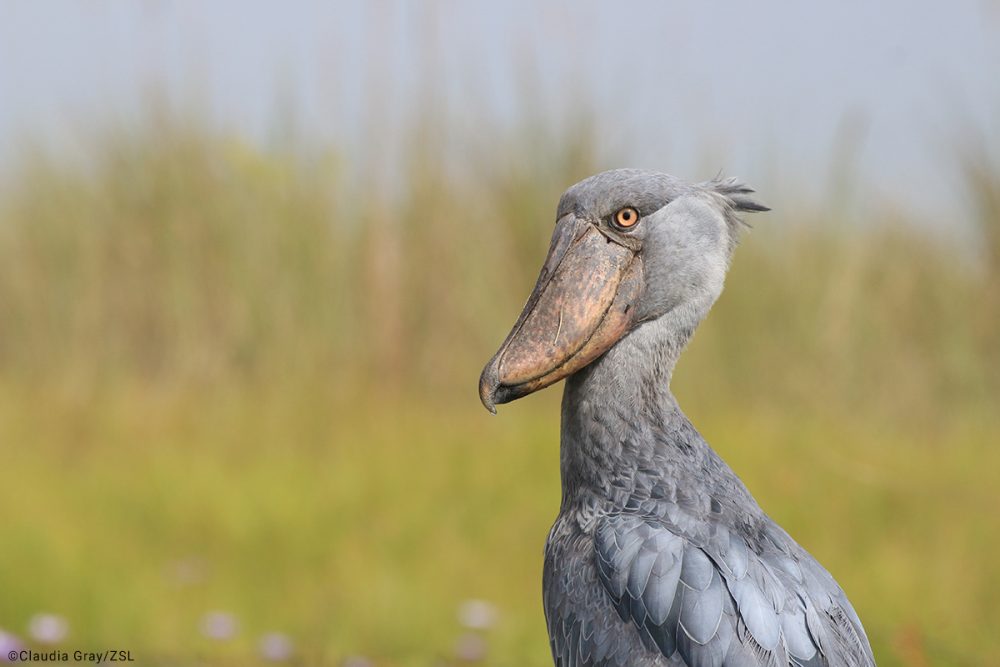
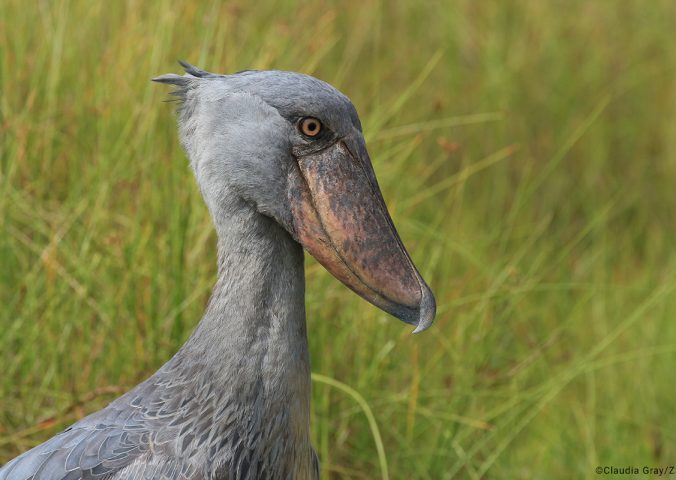
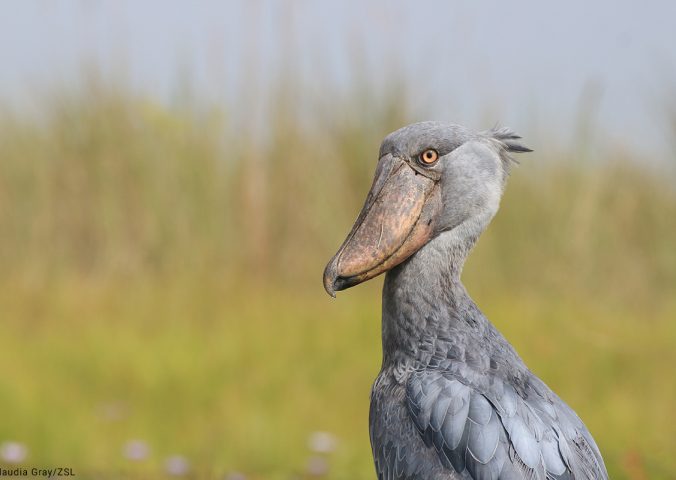
This large waterbird is unmistakable due to its unique ‘shoe-shaped’ bill which gives it an almost prehistoric appearance – reminding us of birds’ dinosaur ancestry.
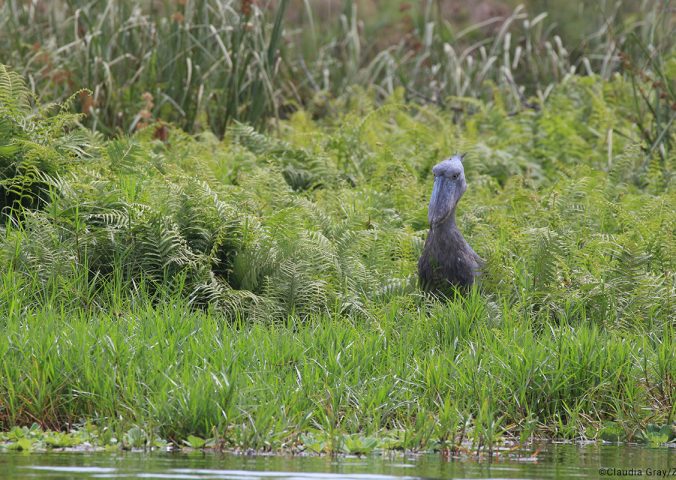
Found in nine countries across Africa the species has a large range, but exists in small localised populations concentrated around swamps and wetlands. Individuals are highly solitary – often the male and female in a breeding pair prefer to occupy different ends of their shared territory.
The nest is large and flattened, built amid swamp grasses or sedges and usually on a mound of floating vegetation or a small island. The construction can be up to three metres wide. Although a clutch of up to three dull, chalky-white eggs is laid, typically only one nestling survives due to inter-sibling rivalry, where the larger (generally first born) chick will out-compete and/or kill its siblings. The breeding season varies, being dependent on Africa’s seasonal flood cycle.
The Shoebill is undergoing a continuing decline owing to the effects of habitat destruction and degradation, pollution, nest disturbance, hunting, and capture for the live bird trade. The global population is currently estimated at between 5,000-8,000 birds and the species is classed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Shoebills are the only member of their genus Balaeniceps, and the only living member of their family, Balaenicipitidae.
- Order: Pelecaniformes
- Family: Balaenicipitidae
- Population: 5,000-8,000
- Trend: decreasing
- Size: 100-140 cm
- Weight: 4-7Kg
EDGE Score
Distribution
The Shoebill’s breeding and resident range is currently estimated to be 1,470,000 km² and includes Burundi, Central African Republic, The Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Rwanda, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia.
Habitat and Ecology
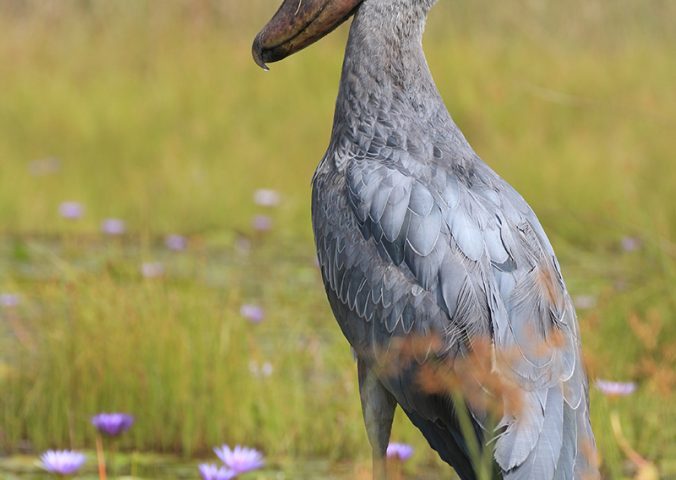
This species’ inhabit wetland habitat, preferring large, seasonally flooded marshes with dense vegetation and areas of floating vegetation often formed by papyrus. They are highly solitary and they forage by ‘walking slowly’ or standing. Large fish such as lungfish are the preferred prey item, but it will feed on a variety of aquatic animals including amphibians, water snakes, young crocodiles, as well as rodents and waterfowl chicks.