About
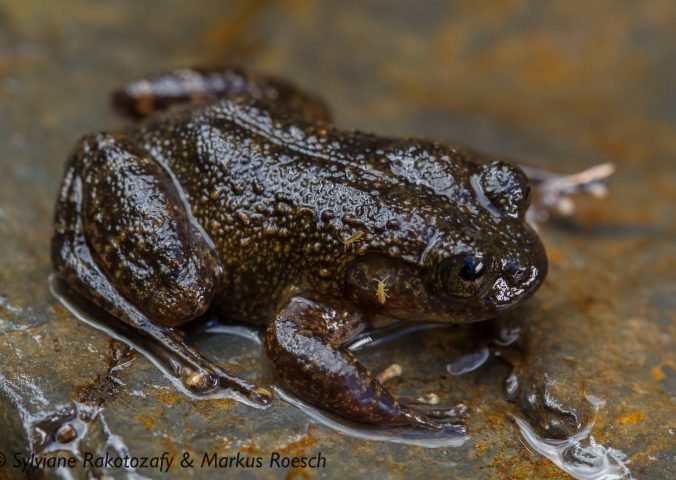
The Critically Endangered Madagascar frog was described in 1974, but was not recorded again for over 40 years until 2010.
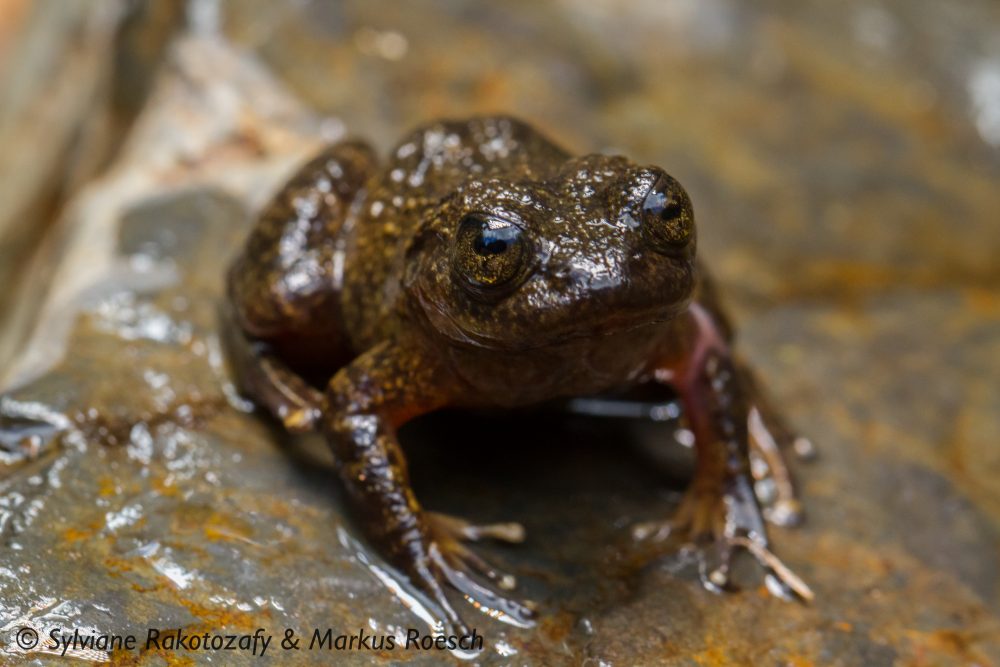
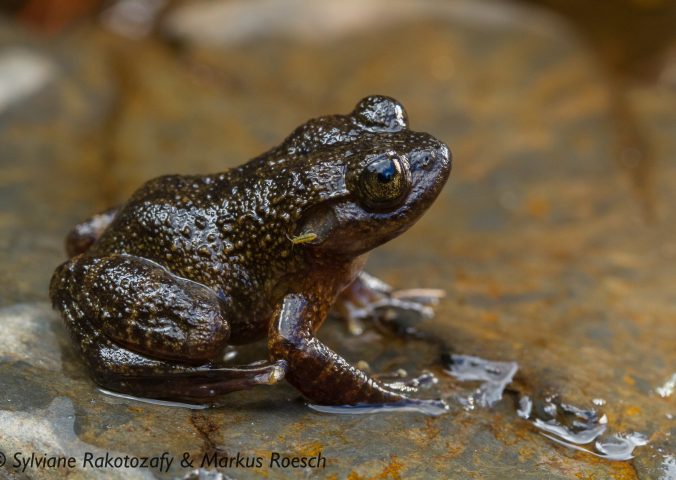
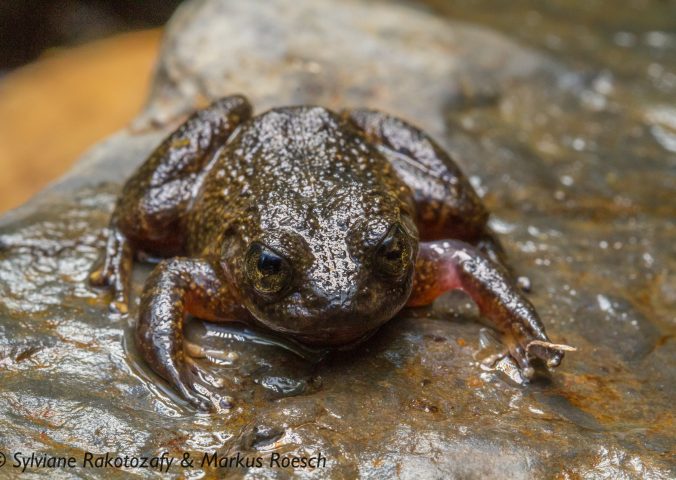
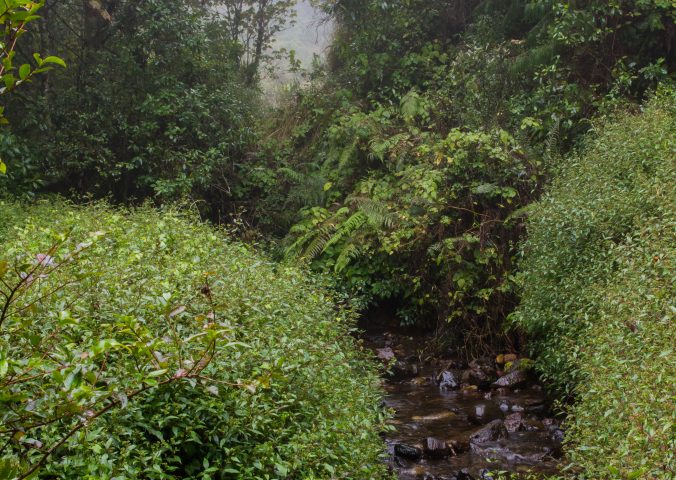
Mantidactylus pauliani is a micro-endemic frog, that lives and breeds in high-altitude streams in the Ankaratra Massif, central Madagascar. Individuals have been found basking during the day on large rocks under a cascade, diving immediately into the water when approached.
The Mantellid frogs diverged from all other amphibian lineages around 65 million years ago, which makes them as distantly related to other frogs as humans are to tarsiers! This species is one of the most threatened amphibians in Madagascar as it lives in a severely degraded habitat that is constantly under threat from annual fires. Moreover, the species is at risk due to illegal logging, expanding agriculture and overgrazing by livestock and charcoal production. All these activities have caused heavy soil erosion and sedimentation which have been responsible for the pollution and siltation of its breeding sites. This species might be threatened also by the presence of the amphibian chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd) across the Ankaratra Massif.
Due to its isolated and restricted distribution at the mountain top, this species is at risk from climate change. Encouragingly, the habitat is now part of the Ankarana Massif Reserve established by the Madagascan conservation organization. The reserve is managed through forest guard units assembled with collaboration with local communities. Local communities are engaged in reforestation efforts intended to improve habitat within the reserve and the amphibian populations on the Massif are subject to ongoing monitoring.
- Order: Anura
- Family: Mantellidae
- Population: Rare
- Trend: decreasing
- Size: 24-34mm
EDGE Score
Distribution
This species is found from a single area within 443 metres of the highest summit of the Ankaratra Massif in central Madagascar at 2,643 metres above sea level. It has also been recorded from three additional sites east of the summit between 2,000-2,285 m above sea level. However, its area of occupancy is believed to be less than 10 km².
Habitat and Ecology
This species is an aquatic frog with its habitat being fast-flowing mountain streams with individuals living and breeding in the fast-flowing streams. They have a maximum longevity of eight years. The Ankaratra Massif is described to harbour residual threatened rainforest fragments, high-altitude savannah and heathland.